Introduction to Linux
Introduction
- Similar to Mac OS, iOS, Windows, and Linux, it is an operating system.
- In actuality, the Linux operating system powers Android, one of the most widely used platforms worldwide.
- The software that controls all of the physical components connected to your laptop or desktop computer is called an operating system.
- In short, the operating system controls how your applications and hardware communicate with one other. Software cannot operate without the operating system (OS).
- The most common operations you carry out on a PC are adding, removing, and transferring files.
- You have two options for managing your files:
- Terminal (Command Line Interface, or CLI)
- The GUI (Graphic user interface)is a file manager.
Launching the CLI on Ubuntu
Two ways to to launch the terminal:
1.go to the Das and type terminal
Launch a Terminal Window From the Dash
You'll find the Terminal application included with your other installed applications. To find them, click the "Show Applications" button at the bottom-left corner of your screen, on the "dash" bar.
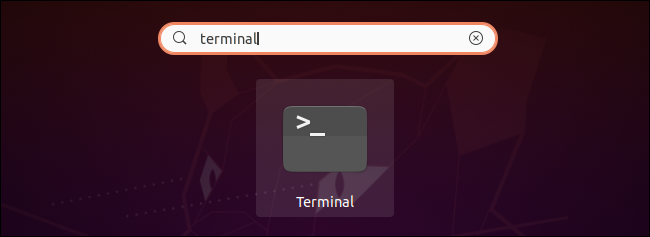
Type "Terminal" and press Enter to find and launch the Terminal shortcut. You can also locate the Terminal icon in the list of all applications that appears here and click it.
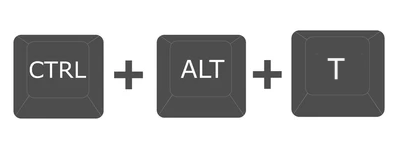
2..by pressing CTRL + ALT + T
Use a Keyboard Shortcut to Open a Terminal
To quickly open a Terminal window at any time, press Ctrl+Alt+T. A graphical GNOME Terminal window will pop right up.
Present working Directory- Directory which is currently browsing is called the Present working directory
- Default, log on to the home directory when the PC is booted
- If you want to determine the directory you are presently working on , use the command – pwd
- pwd command stands for print working directory
- Above figure shows that /home/guru99 is the directory we are currently working on
Present working Directory
- Directory which is currently browsing is called the Present working directory
- Default, log on to the home directory when the PC is booted
- If you want to determine the directory you are presently working on , use the command – pwd
- pwd command stands for print working directory
- Above figure shows that /home/guru99 is the directory we are currently working on
Changing Directories
- To change the current directory, use the 'cd' command
- Consider the following example
- Here, we moved from directory /tmp to /bin to /usr and then back to /tmp
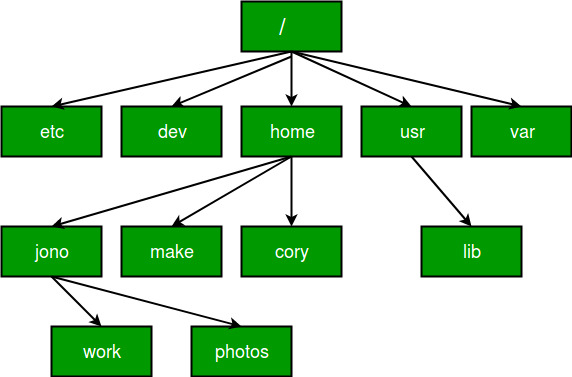
Navigating to Home Directory
- To navigate to the home directory , type the command cd
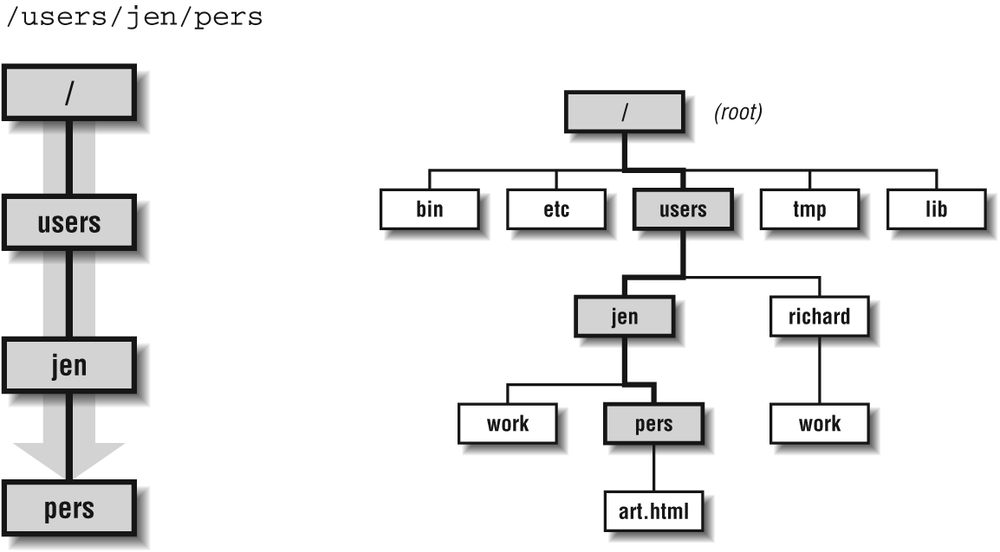
- Root of file system in Linux is denoted by '/'. Similar to 'c:\' in Windows
- Note: Windows use backward slash "\" while in UNIX/Linux , forward slash is use "/"
- Type 'cd /' to move to the root directory.
- A file's position in relation to the current (working) directory* is indicated by a relative path. The position from the root directory is described by an absolute path.
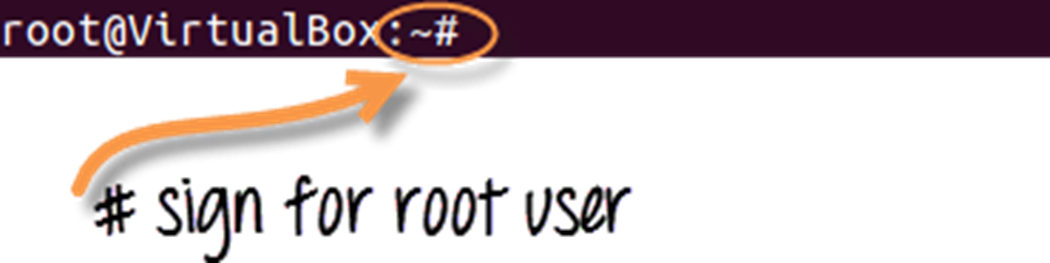






No comments:
Post a Comment